To keep your application data secure from unauthorized access, your application must prove that it is allowed to communicate with Mobile Backend Services (MBS) in each HTTP request. There are two ways your application can do this:
- Application key over SSL
- 2-Legged OAuth
To authenticate user access to individual MBS data objects within your application, such as Photos or Files, you can use access control lists (ACLs). See Access Control Lists for more information.
Application key over SSL
The easiest way to authenticate API requests to MBS is to supply an MBS app key with each request as a URL parameter, for example:
GET https://api.cloud.appcelerator.com/v1/places/search.json?key=<YOUR_APP_KEY> |
MBS defaults to using application key over SSL.
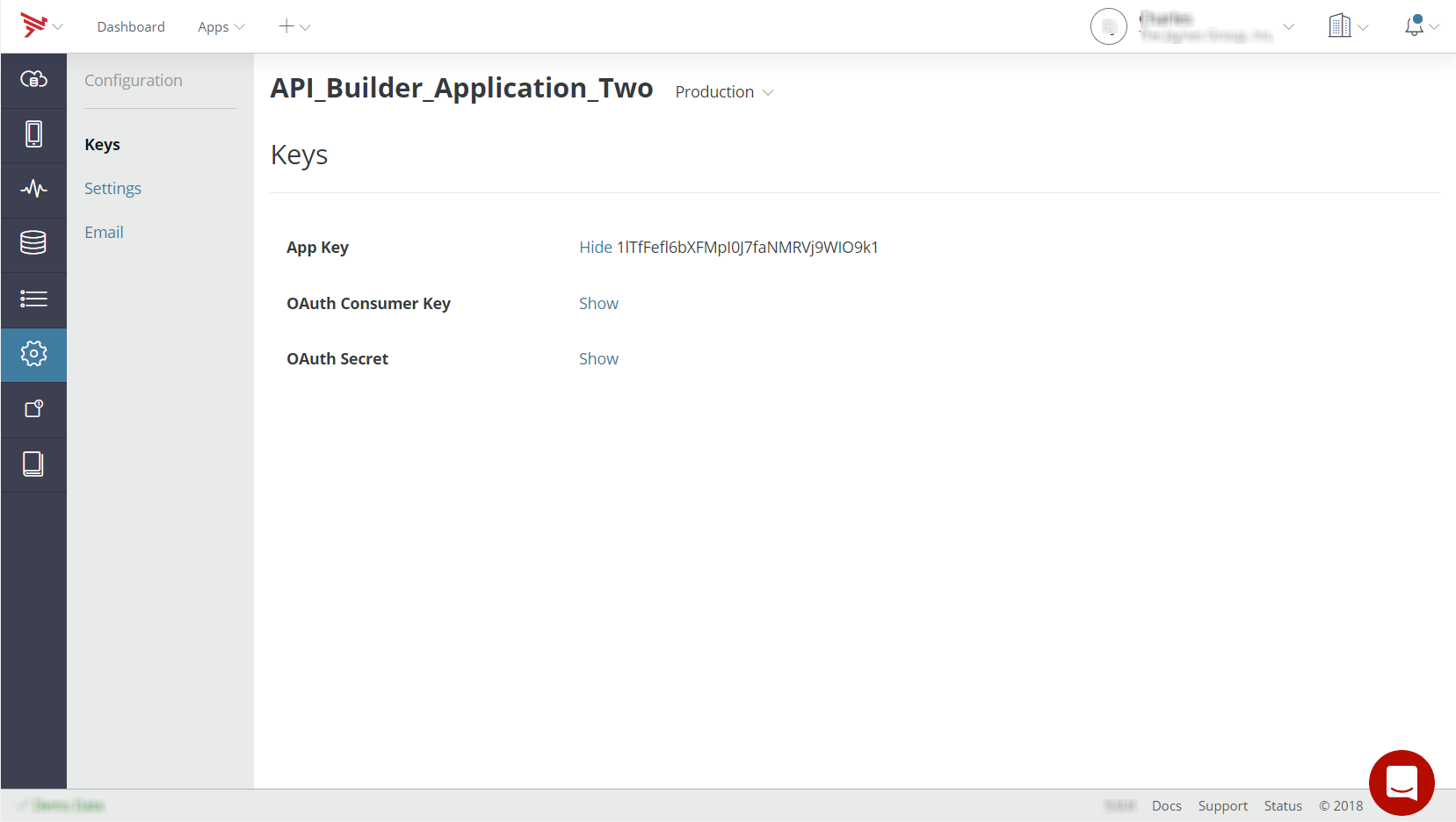
To locate your application key in Dashboard:
- Open Dashboard in your browser and select your MBS application from the Projects view.
-
From the left-hand navigation, select Configuration.
- On the Keys tab, click Show next to the App Key label to show your application key.
2-Legged OAuth
If SSL is not available to the client application, MBS also provides secure authentication via 2-Legged OAuth. In this process, an authentication key and secret are used to sign each request made by your application to MBS. When the MBS server receives the request, the secret and the data sent in the request are used to calculate another signature. If the received and calculated signatures match, the request is processed.
Over a non-SSL connection, OAuth is more secure than the application key approach, as the secret used to generate the signature is known only by the app and the MBS server; it is never sent over the network.
Below is an example of an OAuth HTTP header:
Authorization: OAuth oauth_consumer_key="0685bd9184jfhq22", oauth_token="", oauth_signature_method="HMAC-SHA1", oauth_signature="wOJIO9A2W5mFwDgiDvZbTSMK%2FPY%3D", oauth_timestamp="137131200", oauth_nonce="4572616e48616d6d65724c61686176", oauth_version="1.0" |
To locate your OAuth consumer key and secret in Dashboard:
- Open Dashboard and select your application from the Projects view.
- From the left-hand navigation, select Configuration.
- On the Keys tab, click Show next to the OAuth Consumer Key and OAuth Secret labels.

OAuth example
Most OAuth libraries that support standard (3-Legged) OAuth—such as those
used by Facebook, Twitter, and others—also supports 2-legged OAuth. The
following is an example of making a 2-Legged OAuth request using Ruby.
Provide your MBS OAuth consumer key and secret for the consumer_key and consumer_secret fields. Use an empty string ("") as both the Access Token
and Secret.
require 'rubygems'require 'oauth'# make the consumer out of your secret and keyconsumer_key = ""consumer_secret = ""consumer = OAuth::Consumer.new(consumer_key, consumer_secret, :site => "http://api.cloud.appcelerator.com")# make the access token from your consumeraccess_token = OAuth::AccessToken.new consumer# make a signed request!response = access_token.get("/v1/places/search.json")# show the responseputs response.body |
Access Control Lists (ACLs)
Access Control Lists (ACLs) provide several APIs to implement access control lists for MBS objects. An access control list controls read and write access to MBS objects it's attached to. Please refer to Access Control Lists for more information.